On the Subject of Turbo Cancers
10-10-2023 (Pink background in honor of Breast Cancer Awareness Month).
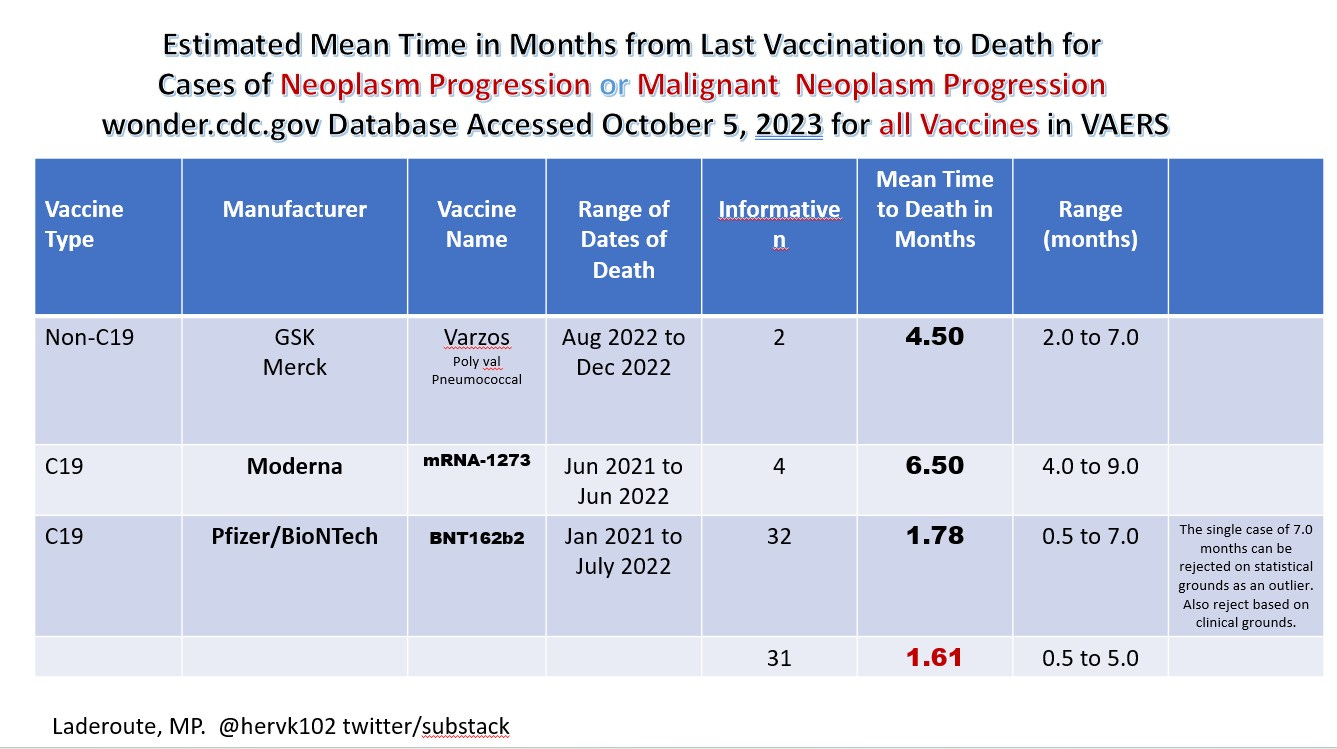
Image 1. Turbo Cancers kill in a few weeks to months whereas normally it would be months to years for many cancers. Here recipients of Pfizer mRNA have a notably shorter survival period for the symptom of “neoplasm or malignant neoplasm progression” than Moderna upon vaccination suggestive that additional significant oncogenic contaminants may be in the PFIZER mRNA shots.
Updated IMAGE 1A. January 12 2025
Updated Image 1A: There were no other cases in the entire VAERS database that had reported either “neoplasm progression” or “malignant neoplasm progression”. Informative cases refers to those cases that provided the onset to death. It is notable that for the informative cases not involving the COVID-19 vaccines that these deaths and onsets occurred during the time that the same were being reported for the COVID-19 vaccines raising the issue that the COVID-19 vaccines could have been at fault.
The medical terms for turbo cancers are neoplasm progression or malignant neoplasm progression.
Updated with new Image 1B. 2025 01 12
IMAGE 1B. Mortality by Cause Analysis Suggests Excess Tumor Deaths at Least in 2021 and 2022 were Tied to SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Infections
Note that the drop off in 2023 for tumor deaths with COVID-19 infections could be due to the fact that they were no longer testing for SARS-CoV-2 (most likely explanation) and/or that spike IgG4 prevailed over the spike IgG1/3 which caused tolerance but secondarily to spike PROTEIN exposures (such as by immunization with any COVID-19 vaccine, or due to shedding).
Note also, that the onset interval of time of diagnosis to death is NOT available in this database so although this refers to excess tumors over 2018 and 2019, it does not necessarily identify them as “turbo cancers”.
McKernan et al, [1] have revealed while both the Pfizer-BioNTech (herein referred to as Pfizer) and Moderna mRNA vaccines (C19 monovalent and bivalent with Omicron variants) have excess cDNA plasmids as contamination, the Pfizer vaccine contains extra components namely the SV40 promoter and its nuclear localization signal in the plasmids which are oncogenic. Most troubling is that these extra oncogenic bits of DNA were not at all required for expression in E. coli. and their inclusion in the lipid-nanoparticles LNPS seems somewhat…sinister. The presence of these SV40 oncogenic sequences was not disclosed to the USA FDA nor to vaccinees. As well we are now learning that the process used to generate the LNPs for the short term clinical trials were made by PCR (no DNA plasmids) whereas for mass vaccination it used a totally different process that included various DNA plasmids. This my dears is fraud.
It is the DNA plasmids which can “genetically modify humans” if integrated into genomic DNA. This is a guess but my guess is that it would be criminal to genetically modify humans, especially without their knowledge or consent.
This means manufacturers and those who authorized, recommended or mandated these vaccines are now fully accountable due to the involved fraud (misrepresentation of the process and purity of the shots used for mass vaccination) and the CRIMINAL genetic modifications of humans [2].
Importantly, these “DNA contamination” findings have been corroborated by a number of laboratories around the world. The findings are uncontested.
What is needed is the evidence of integration of these plasmid sequences in cells or tumors to move forward with lawsuits. The following discussion will reveal some considerations for increasing the chances of detection of these rare tumors.
Most molecular biologists are very concerned about the mRNA vaccines causing turbo cancers either by external influences such as spike protein causing immunosenescence of innate immunity and /or general loss of immunosurveillance; or internally such as insertional mutagenesis when the plasmid sequences are integrated into genomic DNA and/or when spike protein is produced inside the cell.
Following the demonstration in a petri dish that nucleocapsid (n) protein could integrate into a human cell line when a line element sequence was transfected [3], many scientists and clinicians are now very concerned about the genomic integration of bits of DNA from the plasmid contaminants. In particular, the problem of insertional mutagenesis comes to mind, and the risk of turbo cancers. However, what cells might have RT or integrase ?
(Actually no RT is needed as the plasmids are already double-stranded cDNA pieces where smaller pieces are more likely to integrate. So the problem set turns to what cells produce high levels of integrase and what controls this?)
Contributors to Oncogenic Potential
S2 Protein
The S2 protein that is a component of spike, inactivates the tumor suppressors p53, and BRCA1 and 2 [4]. The levels of this protein apparently are much higher after mRNA vaccination than following natural infection. Accordingly, the vaccine derived S2 protein could synergize with the oncogenic plasmids/SV40 sequences also in the mRNA shots providing two hits for the multiple hit hypothesis of cancer [5].
Estrogen is a Carcinogen
Females might be at higher risk of oncogenesis related to mRNA vaccine injections because estrogen although natural is a known carcinogen [6].
Some of the most common genetic alterations leading to cancer involve gene amplification of cancer-causing genes (ERBB2, c-myc), deletions of tumor suppressor genes and translocations.
In the cancer predisposition disorder ataxia telangiectasia (AT) the mutated in AT gene (ATM) fails to adequately control the expression of the guardian of the genome, p53 [7]. Since p53 downregulates alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) [8] the first tumor marker and immunosuppressive factor discovered [9], the unbridled expression of AFP leads to immunosuppression, rapid aging, and to cancers such as lymphomas by early adulthood. Female AT heterozygotes, on the other hand, suffer early onset breast cancer (< 50 years of age).
Interestingly, AT also involves an ionizing radiation hypersensitivity which generates double stranded DNA breaks and where such breaks are known to create gene amplification, deletions and encourage genomic integration [10]. Peculiar to this hypersensitivity is the inability to stop DNA replication at one hour upon exposure to ionizing radiation called radioresistant DNA synthesis (RDS). It is thought this might represent the abnormal DNA synthesis involved in gene amplification. Both deregulated c-myc and AFP are involved in promoting RDS [Laderoute MP, unpublished data] as one might expect. As well, an altered p53 response has been implicated [11].
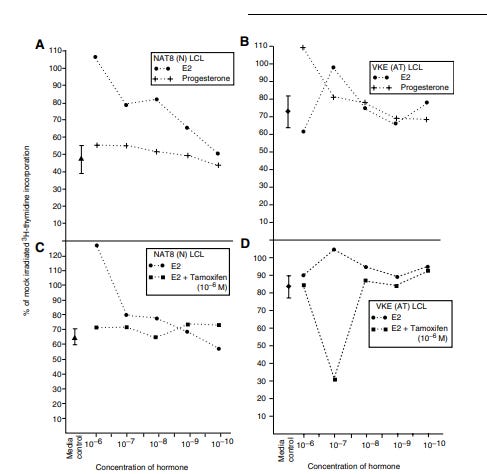
As shown in Image 2 (left side A,C), estrogens (E2 = estradiol) can induce RDS in normal cells (NAT8 lymphocytic cell line) in a dose responsive manner, very analogous to the AT lymphocytic cell line with ATM (VKE lymphocytic cell line) whereas progesterone does not. Note the control conditions for the non-AT cell line shows about a 50% reduction in DNA synthesis at one hour. In contrast for the AT cell line it is about a 25 % reduction. Moreover an excess of tamoxifen (an anti-estrogen) blocks this induction of RDS by estrogen showing indeed it is due to estrogen and estrogen receptors that reprogram gene activation. In contrast for the right panel (B, D) involving AT cells, the levels of RDS are already elevated over the non-AT cell line and not really affected by estrogen except at 10 (-7) M. Only at this E2 dose does tamoxifen block RDS (by about 70%).
Image 2. RDS is Inducible in Non-AT cells by Estrogen and Blocked by Tamoxifen an Anti-Estrogen [12]
Unfortunately, what this may mean is that women may be more susceptible to the cancer causing effects of low dose ionizing radiation especially mammograms but also other radiological imaging techniques, used to diagnose tumors and or complications of COVID-19 [12]. These aspects may synergize with the DNA contaminants for female recipients of the mRNA vaccines.
For neoplasm progression associated with the Pfizer mRNA vaccines (C19 & C19-2) there is a predilection for female sex (Image 3) [13].
Image 3. Where informative, there were 66 Female and 41 Male cases of neoplasm progression for Pfizer (total n=108). For Malignant neoplasm progression, there were 12 Female and 10 Male cases for Pfizer (data not shown) [13].
The malignant neoplasm progression was not as significantly biased towards Pfizer with 23 cases for Pfizer and 10 cases for Moderna. In contrast for neoplasm progression, there were 108 cases for Pfizer versus 4 for Moderna. In the case of Pfizer, the female to male ratio was 1.61 for the neoplasm progression cases. In a cursory examination of types of tumors associated with Pfizer neoplasm progression no particular cancer type was observed [13].
Correlates of Protection Against Cancers
Of the immune cell types that correlate with survival, the INNATE immunity gamma-delta2 T cells provide the top notch correlate of protection (Image 4) [14] even for acute myeloid leukemia [15].
Image 4. The Gamma-Delta2 T cells (INNATE T Cells) Top the List for Best Correlate of Protection Against Tumors [14].
It may be surprising to some that the M1- macrophages (MO) and NK cells were not found to be protective for any or some of these ‘malignant tumors’ (cancers).
In contrast, in terms of COVID-19 it is innate immunity mediated by the lipid body negative foamy macrophages (Image 5) designated WDR74 positive macrophages in the lower respiratory tract [16], the activated sebocytes in the upper respiratory tract [17] or macrophages that respond to and amplify the interferon response during mild disease as shown in humanized mice models [18] which strongly correlate with protection. {Not surprisingly, these are the same cells targeted by SARS-CoV-2 by ADE}.
However, I am not surprised that the study by Gentles et al, 2015 [14] neglected to identify the M1-like MO which produce the protector HERV-K102 particles (Image 5) needed for recovery from mild and moderate COVID-19 but which are lost with severe disease.
Image 5. The INNATE immunity macrophages produce high levels of protector HERV-K102 foamy retrovirus particles in vacuoles which are then released by lysis [19,20].
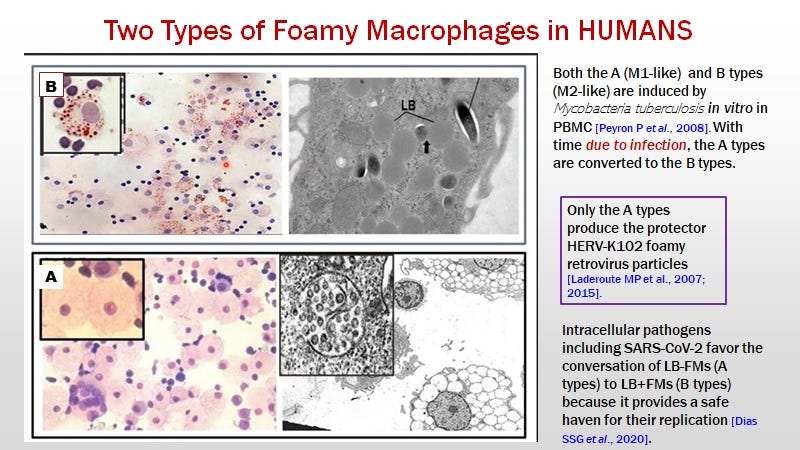
First of all there are two types of foamy macrophages (Image 6) such as induced in vitro by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. TB)[21].
Image 6. Two types of Foamy Macrophages
B= M2-like anti-inflammatory lipid body positive foamy macrophages that stain well with Oil Red O and which provides a safe harbor for pathogen replication in the cytoplasm such as M.TB and many other pathogens including SARS-CoV-2 [21].
A= M1-like, are the lipid body negative (Oil Red O negative) foamy macrophages producing the protector HERV-K102 particles that will lyse to release the HERV-K102 particles [19,20].
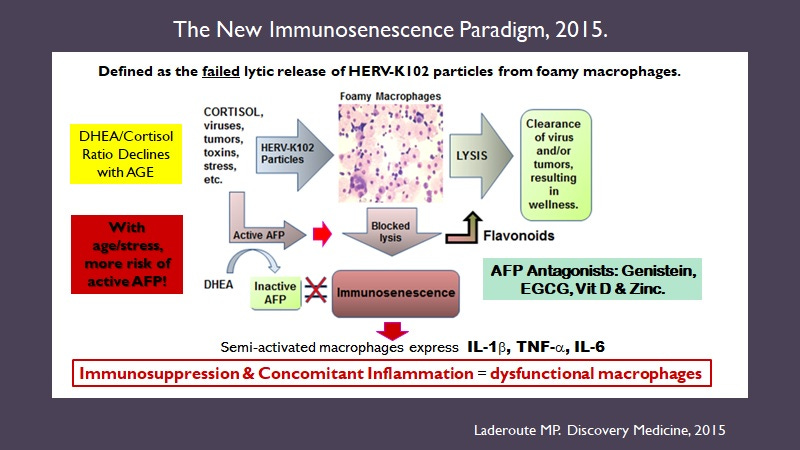
Note that under disease promoting conditions called immunosenescence of macrophages (Image 7) [22] AFP binds to the AFP receptor on the cell surface of macrophages and prevents the lytic release of the protector particles [23,24], where in time these cells will convert to the M2-like anti-inflammatory cells.
Immunosenescence involves both immunosuppression and the release of pro-inflammatory factors which causes chronic disease. Both these attributes are due to AFP binding the AFP receptor on macrophages [23,24]. Such binding generates a negative signal which inhibits apoptosis induction and prevents further differentiation, locking the semi-activated macrophages into continuously releasing the pro-inflammatory factors, IL-1b, IL-6 and TNF-alpha.
To prevent or block immunosenescence of macrophages only AFP antagonists will work. Anti-inflammatories only contribute to the immunosuppression by AFP while pro-inflammatory agents contribute to the problem of pro-inflammation. One must address the cause and not the symptoms of immunosenescence/disease. Known AFP antagonists include vitamin D3, zinc, genistein (isoflavonoids), DHEA [22] or preferably 7-keto-DHEA and more recently, IVERMECTIN [25].
Immunosenescence increases risks of infectious agents and tumors and also contribute to the initiation and progression of many if not most chronic diseases. People with comorbidities often exhibit high blood pressure and/or elevated CRP and these two signs are also signs of immunosenescence of macrophages.
Image 7. The New Immunosenescence Paradigm of Macrophages [22].
In the absence of optimal vitamin D3 levels ( i.e., under conditions presumably provoking the malignant potential of the tumors of Image 3), the protector M1 like foamy macrophages are easily converted to the M2-like which favors pathogen or tumor replication (Image 8) [26].
Image 8. ADE promoting SARS-CoV-2 infection of the LB-FMs Causes a Loss in Trained Innate Immunity
Note that the LB-FMs become factories for the production and release of infectious agents including SARS-CoV-2 [27] or in the TB example above shown in Image 6 [21].
It seems that spike protein also by ADE may cause the conversion of M1 to M2 and loss of trained innate immunity. Thus, vaccination and/or SARS-CoV-2 infection enhances the loss in trained innate immunity providing yet another hit [5] for oncogenesis.
So if the persons with tumors had optimal Vitamin D3 levels in Image 3, this would block either immunosenescence or the conversion of the M1-MO to M2-MO with the result of no malignant tumor and thus, this person would drop out of Image 3. In other words, having a malignant tumor means the M1-MO are dysfunctional related to insufficient Vitamin D3 blood levels. Therefore, they cannot protect as determined in this study of malignant tumors in Image 3, because by definition they are dysfunctional in patients with malignant tumors!
It is tempting to speculate, if the patients in Image 3 were treated with Vitamin D3 to achieve optimal levels, the functional M1-MO would register as very strong correlates of protection (but then you wouldn’t have cancer).
Speculation that the Gamma-Delta2 T cells likely Recognize HERV-K102 Envelope protein
Innate T cells and B cells recognize HERV-K102 envelope and kill tumors and virally infected cells as the envelope becomes expressed on these cells but not on normal cells [reviewed in 28]. Much of the work showing these antibodies and T cells in cancer patients was spearheaded by Wang-Johanning et al since 2002 [reviewed in 28].
Understandably, the antibodies we described in our 2007 paper, were to very specific HERV-K102 envelope peptide sequences [19]. That is to say that these epitopes were unmasked on the HERV-K102 envelope found on the surface of tumors and/or virally infected cells (P61567 envelope protein results from an alternatively spliced transcript for envelope) but masked on HERV-K102 particles (P63135 envelope protein transcribed from the entire genomic sequence). In other words, these innate antibodies do not react with or clear the HERV-K102 particles but will only bind to the cell surface envelope. Since we were the only research group to recognize the significance of this, we stand alone in showing these antibodies were very highly induced in HIV-1 patients [19].
REMARKABLY, the HERV-K102 envelope expressed on the surface of the virus or tumor transformed cells is directly tied to the cell death machinery, and antibodies alone will trigger apoptosis of the tumor or virally infected cells [29].
{These antibodies to HERV-K102 envelope are neutralizing antibodies to any RNA or DNA virus that buds from the cell surface, the so called ‘enveloped’ viruses because when they pick up the membrane when cultured in HUMAN cells, they pick up the HERV-K102 envelope. Non-human cells do not have HERV-K102 envelope so the study of neutralizing antibodies in green monkey does not detect these innate neutralizing antibodies. It is only when pseudotyped virions are produced in human cells for the more popular assays that the innate antibodies to HERV-K102 generate a signal. Unfortunately researchers using these inferior methods claim the neutralizing antibodies to spike correlate with protection against SARS-CoV-2 . In reality it is the innate antibodies (short term) to HERV-K102 envelope that protect.}
In Image 9, it is suggested the HERV-K102 particles released by lysis from the foamy macrophages induce these innate T and B cells. It is not a coincidence that the phosphoantigens recognized by the gamma-delta2 T cells are also commonly induced by M. tuberculosis. As shown in Image 6 M. tuberculosis strongly induces the types of foamy macrophages [21] that produce HERV-K102 particles.
So it is speculated that some of the protector gamma-delta2 T cells that are protective against cancers [14] recognize HERV-K102 envelope.
IMAGE 9. A Plausible Mechanism by Which HERV-K102 Particles Might Auto-vaccinate Innate T cells and B cells with Antigen Receptors for HERV-K HML-2 Envelope
Cross-linking of the antigen receptor on innate T and B cells by HERV-K102 particles may provide signal one, while cGAS-STING [30] may recognize the double-stranded HERV-K102 cDNA released from particles upon entry [19] providing signal two for activation. Consistent with the above is the observation that B and T cell stimulation resulting in the induction of cytokines can be induced by HERV-K HML-2 Env peptides alone ie., in the absence of MHC [31]. This indicates they are innate T responses. That HERV-K102 expression is associated with cGAS-STING activation has been demonstrated in vivo in COVID-19 patients [32]. Indeed, entry of HERV-K102 particles into various cells will trigger an internal ’alternative’ interferon response, circumventing some of the protein protein interactions of virus proteins on host immune responses. It is thought this is how macrophages orchestrate the amplification of the interferon response during mild infections [18].
Evidence that the HERV-K102 Reverse Transcriptase (RT) and Integrase are Active in Foamy Macrophages In Vitro and also In VIVO
In Image 10, the data show the above IMPORTANT concepts relevant to integration of plasmid DNA or SARS-CoV-2 sequences and the potential risks of tumors [3].
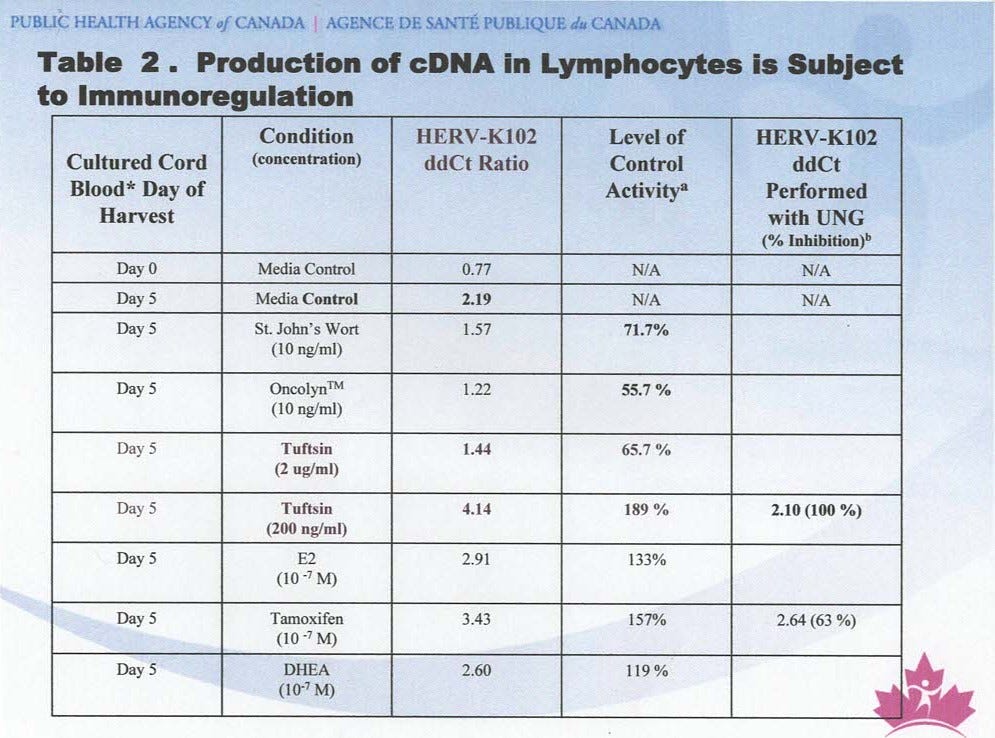
First the method is described in detail in ref 19. It differs from most real time PCRs because there is a confirmatory signal in the middle of what is amplified, meaning at every round of amplification we verify the signal is true and NOT non-specific for both probes (HERV-K102 polymerase gene (pol) and the genomic DNA probe for genomic equivalents, “18S RNA”. It is a ddCt method meaning the ratio of the HERV-K102 pol over genomic equivalents (18S RNA) is provided.
NB the genomes of HERV-K102 particles are cDNA, like most NON-pathogenic foamy retroviruses [19].
It is a ddCt method meaning it assesses the amount of HERV-K102 polymerase DNA signal in DNA isolated from the cultured cells with respect to a gene marker of cell equivalents in this case 18SRNA. So the day 0 ddCt value tells you for this donor, the ratio of HERV-K102 signal per genome is 0.77. By 5 days this signal raises to 2.19. Since the same number is reached when the excess cDNA signal induced by tuftsin is digested by UNG means what is left for analysis is only genomic DNA (ie. the 2.10). In other words at day 5 of culture there is a 3 fold increase in genomic DNA copy number for HERV-K102 pol (2.19/0.77). This shows the active integration of HERV-K102 pol sequences in these foamy macrophages associated with HERV-K102 pro-viral genome replication AS EXPECTED!
NB: at 5 days most of the particles only have RNA genomes (see ref. 20 for this data) as the reverse transcription step for HERV-K102 like all foamy retroviruses occurs at the time of release (and not upon entry into cells like the orthoretroviruses like HIV-1). Lytic release of the HERV-K102 particles occurs on the afternoon on day 7 (or about 6 days into replication initiation).
To further validate these findings a variety of agents were tested.
Tuftsin (TKPR) is a peptide released by bound IgG antibody. At high doses it inhibits HERV-K102 DNA replication and is known to inhibit macrophage activation [33]. At low doses it is known to enhance macrophage activation [33] and here the enhancement of HERV-K102 cDNA replication by tuftsin is 100% related to increased cDNA. This is because the excess signal above the day 5 control is 100% digested by UNG.
St. Johns wort inhibits HERV-K102 replication in vitro and this matches with its ability to completely inhibit HERV-K102 particle production in vivo (at 600 mg/night) [28].
For example a patient with chronic fatigue syndrome who was on St. John’s wort, had no evidence of HERV-K102 particles in plasma (or saliva). However, she had a slightly elevated genomic integration at with a ddCt of 2.0 (normal is 0.88 +/- 0.37 see legend in Image 11). She had been on St. Johns Wort for about 8 years to block insomnia, fatigue and brain fog associated with high levels of HERV-K102 replication. When she went off St. John’s wort, immediately acute insomnia occurred and over the next few days extreme fatigue and brain fog emerged. At 84 hours after stopping St. John’s wort, her ddCt for HERV-K102 DNA particles in plasma was 2.55 x 10 (11) per ml of plasma. Notably all this signal was verified to be particle associated as when the ddCt for DNA was repeated in the presence of UNG (digests all the cDNA of particles but not genomic DNA), the signal returned to 2.0. From this example, one can say:
HERV-K102 replication can be very, very rapid reaching very high levels in just a few days. This is important especially for pandemic viruses and turbo cancers (and arguably, saving humans from extinction).
The combined symptoms of insomnia, fatigue and brain fog may often relate to high levels of HERV-K102. It is notable that these symptoms are featured in long COVID-19 and in C19 vax injuries consistent with the presence of spike protein in monocytes/macrophages up to 15 months after C19 infection. (BTW, these symptoms might be amplified in cases of myeloid dyscrasias associated with Pfizer shots and/or could be made worse by COVID-19 co-infections).
St. John’s wort (hypericum) has been shown to reduce depression in RCTs. Presumably protracted insomnia will lead to depression. So there may be a role in the use of St. John’s wort in Long COVID or in vaccine injury potentially for treatment of insomnia, fatigue, brain fog and/or depression.
Estrogens, anti-estrogens and DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone which binds and inhibits AFP [22]) all enhance HERV-K102 replication.
The data show that the RT and integrase of HERV-K102 is biologically active in vitro in the foamy macrophages as proof of integration is provided.
IMAGE 10. In foamy macrophages, since HERV-K102 replicates its cDNA and also involving integration into genomic DNA, means the reverse transcriptase (RT) and integrase are biologically functional in vitro.
NB: UNG =Uracil N glycosylase which is present in a variant of the mastermix buffer with a product called AmpErase. AmpErase is designed to digest away all cDNA (such as contaminates floating in the lab from other PCR runs). It is used here to digest away all the cDNA found in HERV-K102 particles in the foamy macrophages leaving behind only the genomic DNA for analysis. In the case of low dose Tuftsin, all the signal above the control (4.14 ) for day 5 is digested with the UNG meaning it was all cDNA.
Image 11. Evidence that HERV-K102 integrase and RT are likely active in vivo [20].
Using again the mastermix buffer with UNG, for the DNA isolated from plasma, all the cDNA corresponding to HERV-K102 particles is digested leaving only genomic DNA for analysis. The results show the HESN (HIV-1 exposed seronegative commercial sex workers) who were resistant to HIV-1 acquisition had significantly increased gene copy number (about 5-fold over healthy normal controls) and which was not detected in those who became HIV-1 infected. This shows HERV-K102 integration not occurs in vivo, but this is clinically significant for host defense against pandemic RNA viruses.
This data shows that the RT and integrase of HERV-K102 are likely biologically active in vivo (associated with protection against acquisition of HIV-1, a pandemic RNA virus).
What to look for in terms of integrated plasmid or spike sequences
The above data indicate there may be certain tumors or abnormal macrophages related to the lipid body negative foamy macrophages where both RT and integrase may be expressed and functional. Such tumors could include acute myeloid leukemia (AML), myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) and perhaps salivary gland tumors. The latter is because saliva contains antibodies to HERV-K102 envelope [34] and HERV-K102 particles may be needed for the stimulation of the making and release of these antibodies from innate B cells (Image 9). Therefore some salivary gland tumors may have at some point expressed the RT and/or integrase of HERV-K102 during oncogenesis.
As shown in Image 12, there is some evidence from EudraVigilance (where the database seems much more up to date than the VAERS accessed via wonder.cdc.gov) that there is evidence that Pfizer vaccines present a greater oncogenic risk over Moderna, which persists into 2023.
IMAGE 12. Evidence for increased risk of AML, SGC, HLH and MDS with the Pfizer vaccine which could represent myeloid cells expressing integrase and/or RT.
The progressive increase in the risk ratio of Pfizer over Moderna from 2021 to 2023 for MDS is noteworthy. Moreover it suggests the more the Pfizer doses, the higher the risks. It is also noteworthy that for the HLH and AML cases diagnosed in 2023, the Pfizer cases involved primarily female subjects, but this sex bias was not evident not for MDS cases at any time.
As further evidence of these types of diseases being potentially relevant to the genetic modification of humans by these CONTAMINATED mRNA gene therapy shots, in the wonder.cdc.gov database there were two almost sequential lots for the Pfizer vaccine (ER8734 and ER8736) which presented with symptoms overlapping those in Image 12. ER8734 was also associated with AML recurrent and salivary gland cancers, while ER8736 was associated with with AML, HLH, and MDS. Another lot FC3095 was associated with salivary gland neoplasm and recurrent AML. In another case, lot FF2382 was associated with AML recurrent, AML and HLH. These associations are unlikely to be random events especially considering the sequential lots.
Treatment Options:
Cancers including turbo cancers, infections and chronic diseases should be treated with AFP antagonists, but not with anti-inflammatories because they are immunosuppressive. Many drugs and most if not all herbal medicines are likely immunosuppressive. It is unfortunate that the FDA regulations do not require an assessment of immunosuppressive potential for drug approvals.
{I have always thought that STATIN product monographs (Canada) and product inserts (USA) should carry a black box warning: Danger, statins inhibit trained innate immunity of foamy macrophages needed for protection against infectious agents and cancers. Stop immediately upon onset of infections or cancers and consider not using during pandemics or flu season. }
Known AFP antagonists include vitamin D3, zinc, genistein (an isoflavonoid with anti-estrogen activity useful against any cancers since anti-estrogens reduce cancer mortality irrespective of type [35] ) DHEA/7-keto-DHEA, and now ivermectin [25].
While some have proposed melatonin is good for treating cancer, the biological plausibility that melatonin above 2 mg per night enhances innate immunity is highly unlikely based on its properties illustrated in Image 13. Remember it is innate immunity that correlates with protection against cancers [14,15]!
Image 13. Melatonin Above 2 mg/night becomes immunosuppressive for macrophages and innate immunity.
Melatonin (over 2 mg per night) should be avoided as it blocks the main pathways [36] needed for HERV-K102 particle production in foamy macrophages (which interestingly overlap with malignant phenotypes; I know this part has confused many people).
Summary
Since estrogen is carcinogenic (Image 2), certain cancers or myeloid dyscrasias in association with the exposures to contaminating oncogenic cDNA of COVID-19 vaccines might manifest more commonly in females. By 2023, the incidence of AML, HLH but not MDS as adverse events of the Pfizer COVID-19 mRNA vaccines were dominated by females and where the higher risk of these diseases over Moderna was maintained.
Since estrogen synergizes with ionizing radiation to mediate oncogenesis, women should minimize their mammogram, X-ray and other scanning technology exposures especially when receiving contaminated gene therapy vectors that have been inappropriately called COVID-19 vaccines. However, it would be best to never take any mRNA C19 or other vaccine ever again.
It may be prudent to avoid all vaccines as their safety and effectiveness as well as risk/benefit analyses (such as all cause mortality against placebo controls) have never been assessed.
Pfizer mRNA vaccine female recipients who experienced tumor progression especially upon ionizing radiation scans may represent a useful source for evidence of genetically modified cells from the contaminated mRNA vaccines.
(It has always been deplorable and somewhat ironic to me that during the scan for tumors it could promote oncogenesis such as from mammograms, chest X-rays, CT and PET scans.)
The hunt is on to search for evidence of the integration of plasmid DNA in human recipients of the CONTAMINATED mRNA gene therapy shots. Given that functional reverse transcriptase and integrase are expressed when HERV-K102 replicates to high numbers in the foamy macrophages, means myeloid cell type dyscrasias (abnormalities) may be at higher risk of the manifestation of genomic modification. There are motifs to look for such as the “gggatg” direct repeats and the “tgtg” 5’ starter sequence (Image 14).
IMAGE 14. Telltale signs that HERV-K102 Reverse Transcriptase (RT) and/or Integrase Might be Involved in Plasmid Intergration Into Genomic DNA
BTW, the ultimate proof for a potent role of the HERV-K102 protection system (trained INNATE immunity of foamy macrophages) against cancers, infections and chronic diseases, is the argument that retention of HERV-K102 at 1q22 in humans, may have in part saved Homo sapiens from extinction!
A cursory examination of VAERs and EudraVigilance seems to validate the concerns of excess AML, HLH, MDS and more rarely, salivary gland tumors in victims who received the Pfizer mRNA gene therapy shots with the oncogenic SV40 sequences.
A summary of 3 take home messages can be downloaded here.
REFERENCES:
McKernan, Kevin, Yvonne Helbert, Liam T. Kane, and Stephen McLaughlin. 2023. “Sequencing of bivalent Moderna and Pfizer mRNA vaccines reveals nanogram to microgram quantities of expression vector dsDNA per dose.” OSF Preprints. April 10. doi:10.31219/osf.io/b9t7m.
World Council for Health. Urgent Expert Hearing on Reports of DNA Contamination in mRNA Vaccines, October 9, 2023.
Zhang L, Richards A, Barrasa MI, Hughes SH, Young RA, Jaenisch R. Reverse-transcribed SARS-CoV-2 RNA can integrate into the genome of cultured human cells and can be expressed in patient-derived tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 May 25;118(21):e2105968118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2105968118.
Singh N, Bharara Singh A. S2 subunit of SARS-nCoV-2 interacts with tumor suppressor protein p53 and BRCA: an in silico study. Transl Oncol. 2020 Oct;13(10):100814. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100814.
Wang LH, Wu CF, Rajasekaran N, Shin YK. Loss of tumor suppressor gene function in human cancer: an overview. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(6):2647-2693. doi: 10.1159/000495956.
Das PK, Saha J, Pillai S, Lam AK, Gopalan V, Islam F. Implications of estrogen and its receptors in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2023 Feb;12(4):4367-4379. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5242.
Aguado J, Gómez-Inclán C, Leeson HC, Lavin MF, Shiloh Y, Wolvetang EJ. The hallmarks of aging in Ataxia-Telangiectasia. Ageing Res Rev. 2022 Aug;79:101653. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2022.101653.
Wölfel G, Ostheim E, Staub A, Tümen D, Heumann P, Schmid S, Schlosser S, Müller M, Gulow K, Kunst C. The p53 family of transcription factors represses the alpha- fetoprotein gene expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2023 Sep 29;32(3):346-355. doi: 10.15403/jgld-4055.
Terentiev AA, Moldogazieva NT. Alpha-fetoprotein: a renaissance. Tumour Biol. 2013 Aug;34(4):2075-91. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-0904-y.
Difilippantonio MJ, Petersen S, Chen HT, Johnson R, Jasin M, Kanaar R, Ried T, Nussenzweig A. Evidence for replicative repair of DNA double-strand breaks leading to oncogenic translocation and gene amplification. J Exp Med. 2002 Aug 19;196(4):469-80. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020851.
Laderoute MP. Alterations in p53 do not correlate with radioresistant DNA synthesis. Anticancer Res. 1996 Sep-Oct;16(5A):2825-30. PMID: 8917392.
Laderoute MP. Improved safety and effectiveness of imaging predicted for MR mammography. Br J Cancer. 2004 Jan 12;90(1):278-9; author reply 280. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601442.
Wonder.cdc.gov, VAERS ID October 11 2023. Pfizer mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines 108 Cases of Neoplasm Progression; https://wonder.cdc.gov/controller/saved/D8/D358F987.
Gentles AJ, Newman AM, Liu CL, Bratman SV, Feng W, Kim D, Nair VS, Xu Y, Khuong A, Hoang CD, Diehn M, West RB, Plevritis SK, Alizadeh AA. The prognostic landscape of genes and infiltrating immune cells across human cancers. Nat Med. 2015 Aug;21(8):938-945. doi: 10.1038/nm.3909.
Yue K, Gao H, Liang S, Wu N, Cheng C, Xu LP, Zhang XH, Wang Y, Cheng Y, Huang XJ, Liu J. Improved Vδ2+ T cells recovery correlates to reduced incidences of mortality and relapse in acute myeloid leukemia after hematopoietic transplantation. Ann Hematol. 2023 Apr;102(4):937-946. doi: 10.1007/s00277-023-05125-5.
Ren X, Wen W, Fan X, et al. COVID-19 immune features revealed by a large-scale single-cell transcriptome atlas. Cell. 2021 Apr 1;184(7):1895-1913.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.053.
Ziegler CGK, Miao VN, Owings AH, et al. Impaired local intrinsic immunity to SARS-CoV-2 infection in severe COVID-19. Cell. 2021 Sep 2;184(18):4713-4733.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.07.023
Kenney DJ, O'Connell AK, Turcinovic J, et al. Humanized mice reveal a macrophage-enriched gene signature defining human lung tissue protection during SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell Rep. 2022 Apr 19;39(3):110714. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110714.
Laderoute MP, Giulivi A, Larocque L, Bellfoy D, Hou Y, Wu HX, et al. The replicative activity of human endogenous retrovirus K102 (HERV-K102) with HIV viremia. AIDS. 2007 Nov 30;21(18):2417-24.
Laderoute MP, Larocque LJ, Giulivi A, Diaz-Mitoma F. Further evidence that human endogenous retrovirus K102 is a replication competent foamy virus that may antagonize HIV-1 replication. Open AIDS J. 2015 Dec 7;9:112-22. doi: 10.2174/1874613601509010112.
Peyron P, Vaubourgeix J, Poquet Y, Levillain F, Botanch C, Bardou F, et al. Foamy macrophages from tuberculous patients' granulomas constitute a nutrient-rich reservoir for M. tuberculosis persistence. PLoS Pathog. 2008 Nov;4(11):e1000204. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000204.
Laderoute MP. A new paradigm about HERV-K102 particle production and blocked release to explain cortisol mediated immunosenescence and age-associated risk of chronic disease. Discov Med. 2015 Dec;20(112):379-91.
Laderoute MP. The Characterization of a Novel, Widespread, PNA-Reactive Tumor Associated Antigen; The Alpha-fetoprotein Receptor/ Binding Protein. University of Alberta Ph.D. Thesis, January 7, 1991, pp256. https://era.library.ualberta.ca/items/6f548eb6-49a2-456c-b472-41f68976077f.
Laderoute MP, Pilarski LM. The inhibition of apoptosis by alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and the role of AFP receptors in anti-cellular senescence. Anticancer Res. 1994 Nov-Dec;14(6B):2429-38.
Laderoute M. Ivermectin may prevent and reverse immunosenescence by antagonizing alpha-fetoprotein and downmodulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR hyperactivity. Open Heart, April 29, 2021.
Oh J, Weng S, Felton SK, et al. 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D inhibits foam cell formation and suppresses macrophage cholesterol uptake in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2009 Aug 25;120(8):687-98. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.856070.
Dias SSG, Soares VC, Ferreira AC, et al. Lipid droplets fuel SARS-CoV-2 replication and production of inflammatory mediators. PLoS Pathog. 2020 Dec 16;16(12):e1009127. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009127.
Laderoute MP. Clues to finding correlates of risk/protection for HIV-1 vaccines [version 2; peer review: 2 approved with reservations] F1000 Research 2018, 6:868. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.11818.2.
Wang-Johanning F, Rycaj K, Plummer JB, Li M, Yin B, Frerich K, Garza JG, Shen J, Lin K, Yan P, Glynn SA, Dorsey TH, Hunt KK, Ambs S, Johanning GL. Immunotherapeutic potential of anti-human endogenous retrovirus-K envelope protein antibodies in targeting breast tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012 Feb 8;104(3):189-210. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djr540.
Decout A, Katz JD, Venkatraman S, Ablasser A. The cGAS-STING pathway as a therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021 Sep;21(9):548-569. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00524-z.
Arru G, Galleri G, Deiana GA, et al. HERV-K modulates the immune response in ALS patients. Microorganisms. 2021 Aug 23;9(8):1784. doi: 0.3390/microorganisms9081784.
Guo Y, Yang C, Liu Y, et al. High expression of HERV-K (HML-2) might stimulate interferon in COVID-19 patients. Viruses 2022, 14, 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ v14050996.
Siemion IZ, Kluczyk A. Tuftsin: on the 30-year anniversary of Victor Najjar's discovery. Peptides. 1999;20(5):645-74. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(99)00019-4.
Apostolou E, Rizwan M, Moustardas P, et al. Saliva antibody-fingerprint of reactivated latent viruses after mild/asymptomatic COVID-19 is unique in patients with myalgic-encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome. Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 20;13:949787. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.949787.
Fisher B, Costantino JP, Wickerham DL, Redmond CK, Kavanah M, Cronin WM, Vogel V, Robidoux A, Dimitrov N, Atkins J, Daly M, Wieand S, Tan-Chiu E, Ford L, Wolmark N. Tamoxifen for prevention of breast cancer: report of the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project P-1 Study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998 Sep 16;90(18):1371-88. doi: 10.1093/jnci/90.18.1371.
Talib WH, Alsayed AR, Abuawad A, Daoud S, Mahmod AI. Melatonin in cancer treatment: current knowledge and future opportunities. Molecules. 2021 Apr 25;26(9):2506. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092506.














Thank You, Dr. Laderoute. This is terribly important. People need to notice. I keep pointing it out.
This is horribly abnormal, so many young women with no discernible risk factors are dying of rapidly advancing cancers. It was never like this before the shots.
Thanks for your research and reporting!
I am for preventing breast cancer and for treatment research, but i must bring to your attention that "Breast Cancer Awareness Month" and the pink marketing campaign are a creation of the pharmaceutical/chemical industry. https://www.bcaction.org/pink-ribbon-marketing-culture/the-cancer-industry/ This organization cautions people to check how their donations are directed. Prevention is far more cost effective and life-affirming than cure!